
Article
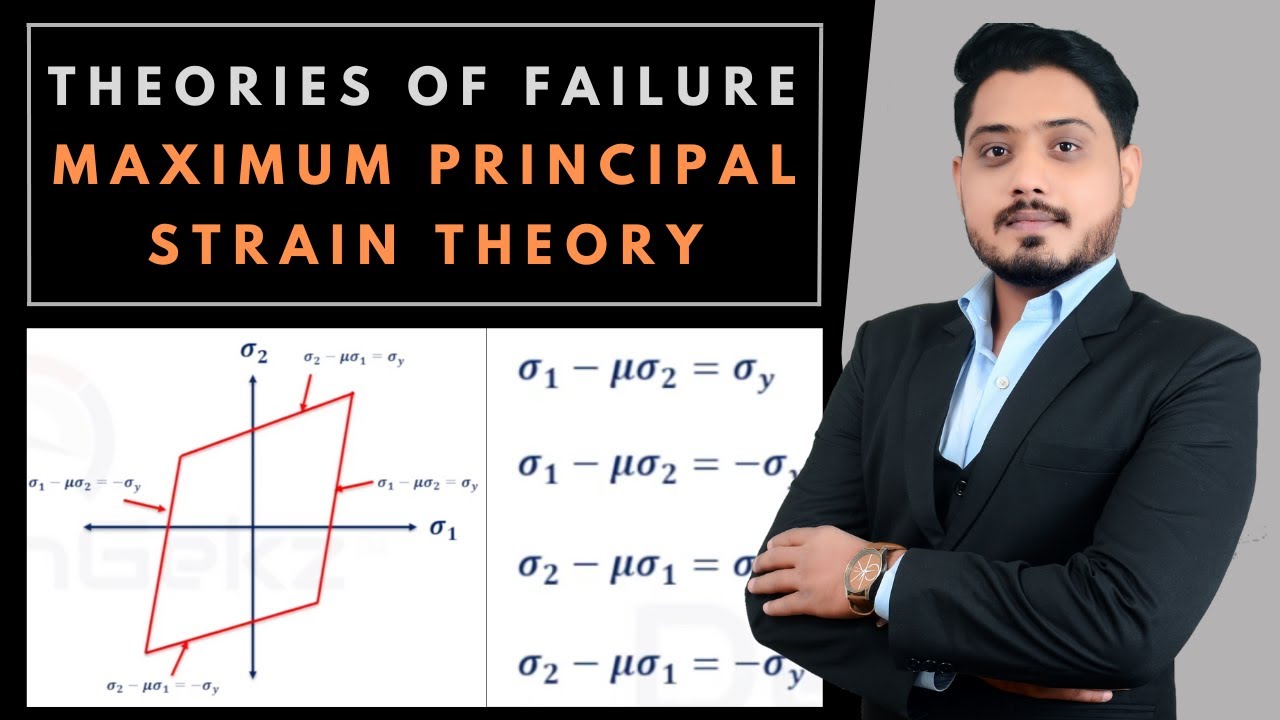
Maximum principal strain theory. Maximum principal (or normal) strain theory is also known as Saint Venant theory. Failure occurs at a point in a machine member when the maximum principal strain in a bi-axial stress system reaches the limiting value of strain in a simple tension test. Limiting strain means the yield point of the material.
SOLVED QUESTION THREE (a) Explain the following failure theories and sketch the corresponding
1. Maximum normal stress theory: This theory states that failure occurs when the maximum normal stress in a material exceeds its ultimate tensile strength (UTS). The UTS is the maximum stress a material can withstand before it fails. This theory is applicable to brittle materials such as ceramics and glass. 2.

(PDF) Application of Maximum Principal Strain Theory for Study of Coal Particle Disintegration
Jul 31, 2021 — by ML Engineering Content Editor in Engineering This is the corresponding failure theory to maximum normal stress theory in which the principal strain values of a point are used. This theory is also applicable to brittle materials such as cast iron.

Maximum principal stress theory Being Learning YouTube
The maximum-principal-stress criterion (86) postulates that the growth of the crack will occur in a direction perpendicular to the maximum principal stress. As a continuous criterion, the criterion does not take into account the discreteness of the numerical modeling of the crack-extension procedure.

Maximum Principal Strain Theory & Problem Lecture 03 YouTube
The Maximum Principal Strain Theory, also known as the Saint-Venant Theory, is a theory of failure in the field of strength of materials. It states that failure occurs when the maximum principal strain in a material exceeds its failure strain. This theory focuses on the measurement of strain, which represents the deformation of a material, and.

Lecture1819 Theories of Failure Maximum Shear Stress Theory (Guest Tresca Theory) Maximum
(c) Maximum Principal strain theory : This Theory assumes that failure occurs when the maximum strain for a complex state of stress system becomes equals to the strain at yield point in the tensile test for the three dimensional complex state of stress system. For a 3 - dimensional state of stress system the total strain energy U t
Maximum Principal Strain Theory of Failure St Venant's Theory Jagadish Atole Designgekz
The equation to calculate the maximum (major) principal strain is given by, ɛ1 = ɛx + ɛy 2 + √(ɛx - ɛy 2)2 + (γxy 2)2 Where, ɛx, ɛy = Normal strain in x and y direction respectively γxy = Shear strain The equation for the minimum (minor) principal strain is given by, ɛ2 = ɛx + ɛy 2 - √(ɛx - ɛy 2)2 + (γxy 2)2

Maximum principal strain following a severe lateral impact. Download Scientific Diagram
The maximum strain failure criterion is unified with the maximum stress failure criterion, after exploring the implications of two considerations responsible for this: (1) the failure strains for the direct strain components employed in the maximum strain criterion are all defined under uniaxial stress states, not uniaxial strain states, and (2).

Maximum Principal Strain Theory YouTube
1. Maximum tensile stress theory (the first strength theory is the maximum principal stress): This theory is commonly referred to as the first strength theory. It holds that the primary cause of failure is the maximum tensile stress.

MAXIMUM PRINCIPAL STRAIN THEORY YouTube
Maximum Principal Strain Theory. This theory states that the failure or yielding occurs at a point in a member when the maximum principal ( or normal ) strain in a bi-axial stress system reaches the limiting value of strain which means strain at the yield point as determined from a simple tensile test.

Maximum principal strain strain values calculated by the model and... Download Scientific Diagram
Maximum Principal stress theory or Maximum normal stress theory Maximum principal strain theory Maximum shear stress theory 4. Maximum strain energy theory 5. Maximum shear strain energy theory or Distortion energy theory Design conditions for various failure theory GATE PREVIOUS QUESTIONS AND SOLUTIONS

Maximum Principal Strain Theory Engineering Mechanics Being Learning YouTube
Max. principal strain theory "Failure occurs at a point in a body when the maximum strain at that point exceeds the value of the maximum strain in a uniaxial test of the material at yield point" 'Y' - yield stress in uniaxial tension, yield [email protected] Ramadas Chennamsetti 17 strain, εy = Y/E The maximum strain developed in.

Maximum principal strain e 1 and minimum principal strain e 2 (in... Download Scientific Diagram
What is Principal Stress? Principal stress represents the maximum and minimum normal stresses that occur within a material when subjected to complex loading conditions. It is essential to understand this concept as it provides insights into the material's response and its potential points of weakness.
Maximum and minimum principal strains for both exvivo experiments, and... Download Scientific
We will study four important failure theories, namely (1) maximum shear stress theory, (2) maximum normal stress theory, (3) maximum strain energy theory, and (4) maximum distortion energy theory. Out of these four theories of failure, the maximum normal stress theory is only applicable for brittle materials, and the remaining three theories.
Images of maximum principal strain (mm) on piston tip from each model... Download Scientific
According to the theory of maximum principal strain, "The failure of a material or component will occur when the maximum value of principal strain developed in the body exceeds the limiting value of strain i.e. value of strain corresponding to the yield point of the material". Maximum principal stress theory is also termed as Saint Venant theory.

Maximum Principal Strain Theory Saint Venant's Theory Principal Strain Theory Machine
Material failure theory is an interdisciplinary field of materials science and solid mechanics which attempts to predict the conditions under which solid materials fail under the action of external loads. The failure of a material is usually classified into brittle failure ( fracture) or ductile failure ( yield ).